We live in a digital age where information is at our fingertips 24/7, and the internet offers a level of anonymity that makes it easy to spread false news and information, whether accidentally or deliberately.
Fake news refers to distorted and sometimes falsified reports with the intention to mislead. The concept originally referred specifically to political reports, but has now expanded to generally mean intentionally inaccurate information.
! Note !: Journalists can report on a story that naturally develops; sometimes in the process the information changes. That is not fake news. A journalistic story has the intention of providing the most accurate information available at that time. Fake News intends to mislead.
Terms as defined by the Oxford Learner's Dictionary:
Other related terms:
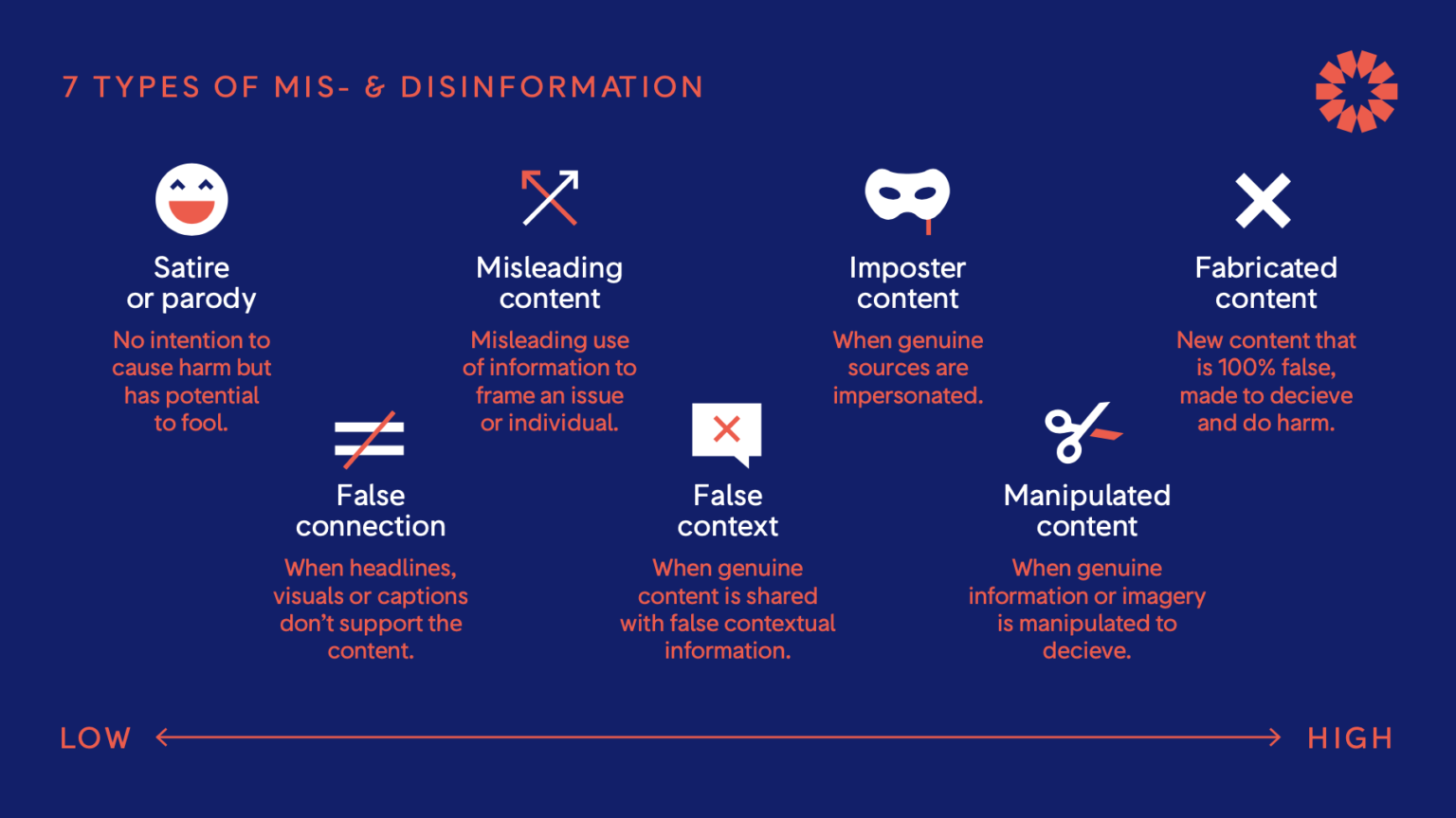
Wardle, Claire. "Understanding information disorder." First Draft News, 22 Sept 2020, https://firstdraftnews.org/long-form-article/understanding-information-disorder/
7 Types of Mis- and Disinformation:
From lowest to highest:
 How Algorithms Create and Prevent Fake News
by
Noah Giansiracusa
How Algorithms Create and Prevent Fake News
by
Noah Giansiracusa
 COVID-19, Racism and Politicization
by
Kalinga Seneviratne; Sundeep R Muppidi
COVID-19, Racism and Politicization
by
Kalinga Seneviratne; Sundeep R Muppidi
 Lie Machines
by
Philip N. Howard
Lie Machines
by
Philip N. Howard
 Misinformation Matters
by
Uyiosa Omoregie, Kirsti Ryall
Misinformation Matters
by
Uyiosa Omoregie, Kirsti Ryall
 The Politics of Social Media Manipulation
by
Richard Rogers (Editor); Sabine Niederer (Editor)
The Politics of Social Media Manipulation
by
Richard Rogers (Editor); Sabine Niederer (Editor)
This guide was created by Ontario Tech Libraries and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License, except where otherwise noted.
